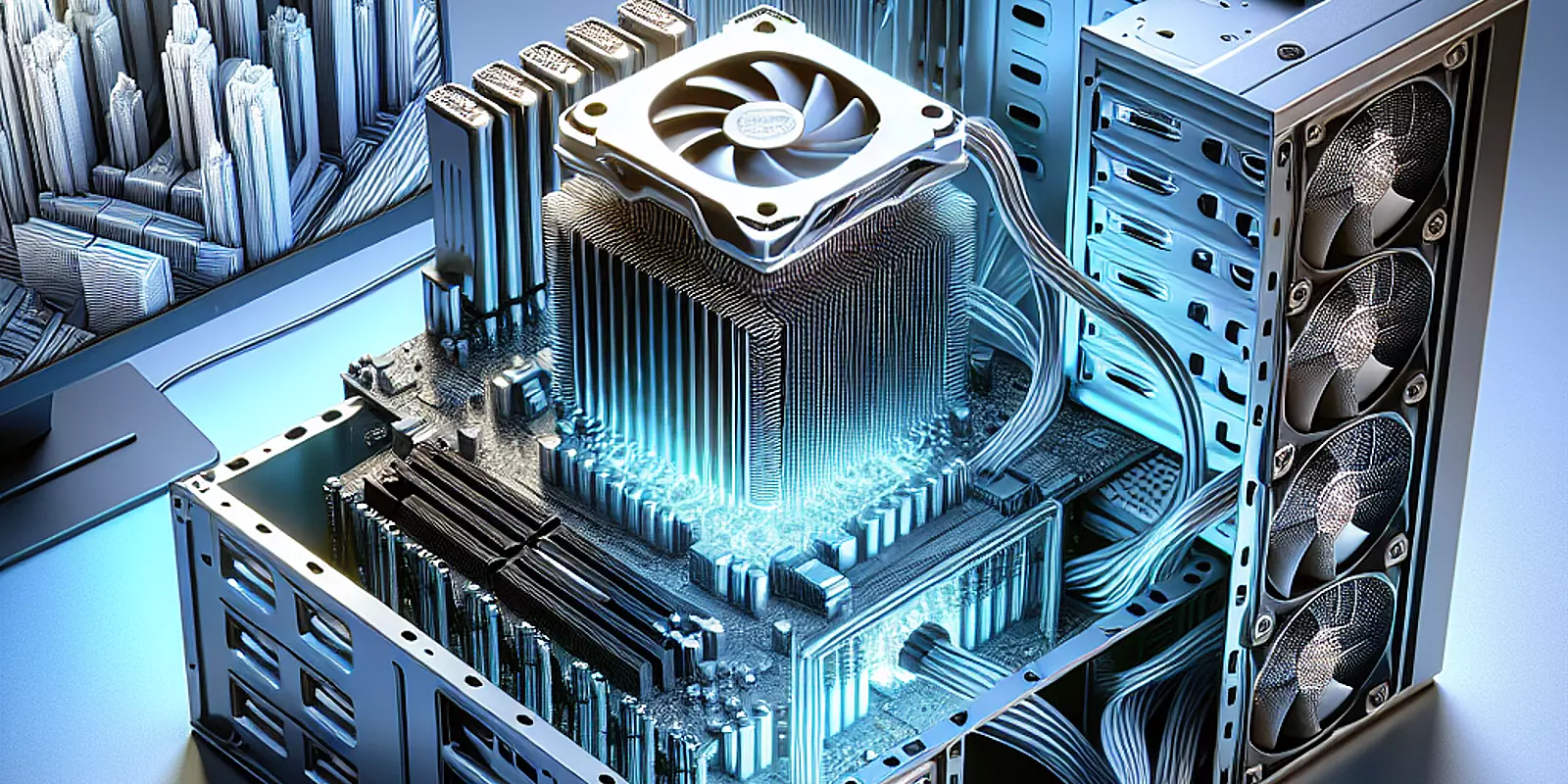
In the ever-advancing field of architectural rendering, the need for robust CPUs is more crucial than ever. As professionals tackle complex projects using powerful software like Corona Renderer, they often face a significant hurdle: CPU overheating. High-performance processors, such as the Intel 12700K, are essential for complex visualizations but also significantly strain the system, making efficient CPU cooling solutions vital to maintain peak performance and prevent hardware failure.
CPU overheating is a major concern that often goes unnoticed until performance starts to drop, causing frustration among professionals. Intensive rendering software demands extensive computational resources, which leads to high thermal output that can surpass safe operating temperatures. Factors contributing to this include complex algorithms, large data processes, and inadequate cooling systems. Given that modern CPUs produce more heat due to increased clock speeds and core counts, understanding the causes of overheating is key for anyone seeking to improve CPU performance.
In architectural rendering, the intense demand on CPU power is substantial. Powerful CPUs, like the Intel 12700K, are pushed to their operational limits, highlighting the necessity of effective cooling strategies. Not only can these strategies prevent overheating and prolong hardware life, but they can also significantly enhance system performance. Here are some important steps to optimize CPU cooling:
Efficient Thermal Paste Application: Correct application of thermal paste is crucial for efficient heat transfer from the CPU to the cooler, maintaining optimal temperatures.
Choosing the Right Cooling System: Upgrading from stock coolers to advanced air or liquid cooling systems can greatly improve heat dissipation, serving as a vital solution to CPU cooling requirements.
Controlling Ambient Temperature: Keeping the workspace cool helps lighten the load on CPU cooling systems, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Awareness of Hardware Limits: Knowing your CPU's thermal thresholds is essential for planning and executing rendering tasks effectively.
By addressing these areas, professionals engaged in architectural rendering can achieve improved system performance and extend their hardware's lifespan even under demanding conditions.
Effective CPU cooling is critical for achieving superior quality in architectural rendering. As professionals push their creative limits, understanding and implementing efficient cooling solutions is increasingly necessary. By utilizing the strategies discussed above, professionals can ensure a balance of excellent performance and hardware sustainability during intense rendering sessions. These solutions empower creative tools, allowing professionals to focus more on innovation and less on hardware constraints, making CPU cooling not just necessary but transformative in performance enhancement.